Extraordinary ferromagnetic coupling and magnetodielectric phenomena in NiO nanoparticles
Subir Roy, Rajesh Katoch, and S. Angappane
IEEE-Trans. Magn. 55 (2018); DOI: 10.1109/TMAG.2018.2865678
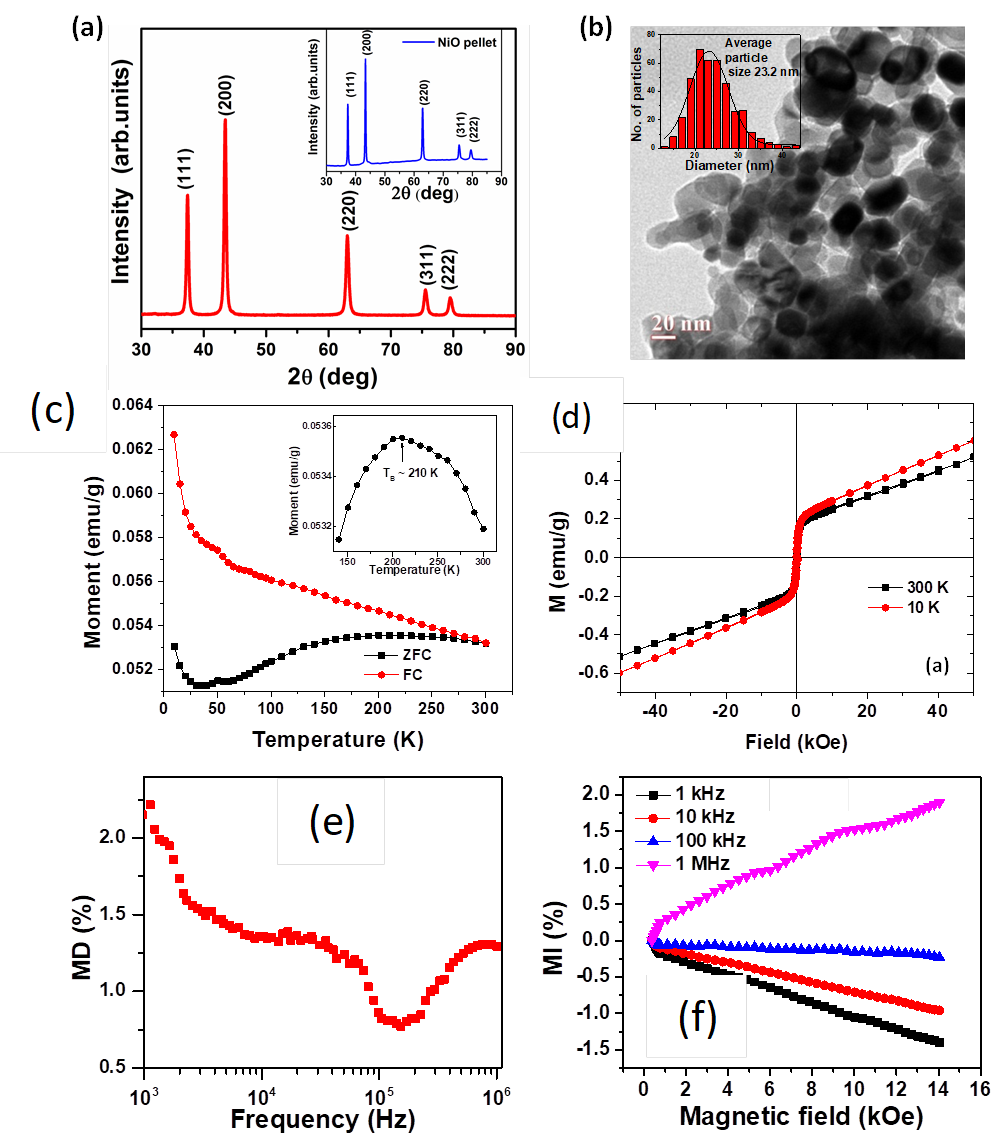
(a) X-ray diffraction data and (b) TEM image with particle size distribution of NiO nanoparticles. Inset of (a) shows the XRD data of NiO nanocompact. (c) FC-ZFC magnetization curves and inset shows blocking temperature (TB), (d) M-H loops of NiO nanoparticles at 300 and 10 K. (e Variation of magnetodielectric effect with frequency, (f) magnetoimpedance as a function of magnetic field at different frequencies.
We intend to understand the ferromagnetism and magnetodielectric phenomenon in NiO nanoparticles with average diameter ~ 23 nm synthesized by chemical route. Magnetic studies revealed that NiO nanoparticles are weakly ferromagnetic. Notably, temperature dependent magnetization studies show a bifurcation of the FC-ZFC curves, suggesting a competition between FM and AFM interactions with blocking temperature (TB) at ~ 210 K. Additionally, we observed field dependent exchange bias effect in the nanoparticles. Further magneto-dielectric studies revealed that the changes in the dielectric constant and loss induced by the magnetic field are strongly frequency-dependent, which originates from combined effect of extrinsic Maxwell–Wagner polarization along with magnetoresistance. It was found that the magnetoimpedance changes sign from negative at low frequencies to positive at higher frequencies of excitation signal. Cole-Cole studies showed that the negative magnetoimpedance at low frequencies arises from ferromagnetic surface/grain boundary and positive magnetoimpedance at higher frequencies originates from antiferromagnetic core of NiO nanoparticles.